Deep Neural Network (Rede Neural Profunda)
Perceptron
The perceptron was invented by Frank Rosenblatt in 1957. Perceptrons are important in deep learning because they laid the foundation for more complex neural networks. The concept of the perceptron was inspired by the understanding of the human brain, specifically mimicking the way neurons function.
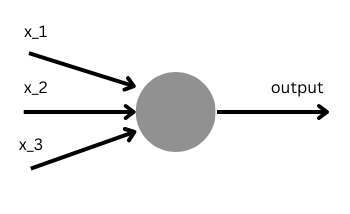
Rosenblatt proposed a simple rule to calculate the output. Here,
Thus, the perceptron can act as a binary classifier. The threshold essentially decides the output of the neural network.
How a Perceptron Works: I'll explain with an example
Imagine you want to marry a girl. There are three conditions:
- Occasionally, she does stupid things.
- She doesn't have a pet.
- She is either Dutch or German.
Now, we can represent these as
- Doing stupid things is 1; not doing stupid things is 0.
- Having a pet is 1; not having a pet is 0.
- Being Dutch or German is 1; other nationalities are 0.
You can have weights associated with these priorities. For example:
3 has a weight of 7
2 has a weight of 3
1 has a weight of 2
And the threshold is, let's say, 6. You see, even if conditions 2 and 1 are true, which is the weight of two times input of two plus the weight of one times input of one, i.e., 3x1 + 2x1, it still doesn't meet the threshold; it's less or equal to 6, so the model is going to predict 0, which means I won't end up getting married, lol.
But if the 3rd condition is true, i.e., 1x7 = 7, which is higher than 6, then I'll end up getting married. This is so simplistic, but it is what it is, lmao. The model is going to end up predicting 1. I'll get married.
Sigmoid Neurons: Let's dig deeper
Small changes in weight and bias should only make small changes in output. However, that's not the case with a single perceptron; a small change in w/b can cause the output to completely predict the wrong value. To resolve this issue, we introduced sigmoid neurons. Sigmoid neurons are similar to perceptrons but are modified so that small changes in w/b cause only a small change in output, i.e.,
Also, unlike a perceptron, a sigmoid neuron can output probabilities, so not just 0 and 1. The output of a sigmoid function is defined by
The output of a sigmoid neuron is mathematically represented by applying the sigmoid activation function to the weighted sum of its inputs plus a bias term. The sigmoid function,
The weighted sum,
where:
are the weights associated with each input , are the input values to the neuron, is the bias term, is the base of the natural logarithm, approximately equal to 2.71828.
Combining these, the output of a sigmoid neuron,
Shape of sigmoid
This equation captures the entire process of calculating the output of a sigmoid neuron, from combining inputs with their weights, adding a bias, and passing the result through the sigmoid function to produce an output in the range (0, 1). This output can be interpreted as a probability in the context of binary classification problems, making sigmoid
The sigmoid graph, characterized by its smooth S-shaped curve, represents the sigmoid function, which is mathematically defined as
